Deploy with Git
With the Git integration feature, ThoughtSpot provides the ability to connect ThoughtSpot Orgs to a Git repository, push TML files on demand to Git branches, and deploy commits from branches back into ThoughtSpot.
Git integration in ThoughtSpot provides:
-
Version control via REST API or within the UI
-
Development and deployment workflows via REST API
|
Note
|
ThoughtSpot currently supports integrating with GitHub / GitHub Enterprise. |
Git integration overview🔗
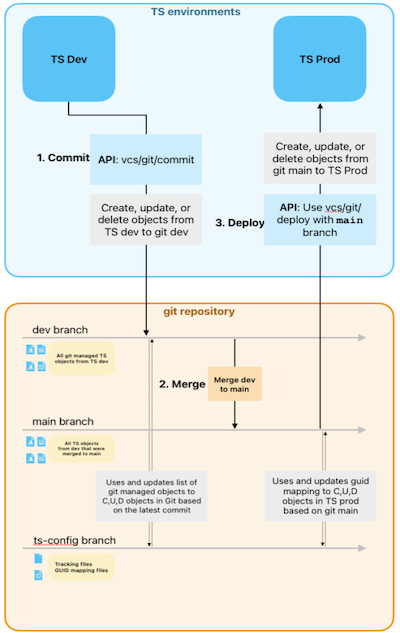
Git integration is best thought of as linking a Git branch to a ThoughtSpot Org, using the configure Git integration REST API.
A paired Git branch and ThoughtSpot Org are called an environment.
Environments do not have to be on the same ThoughtSpot instance - you may have an environment on a "dev instance" that deploys to any number of "environments" on any number of "prod instances".
ThoughtSpot provides REST API for exporting TML from ThoughtSpot Org into a linked Git branch (committing into Git) and for importing TML from a linked Git branch into the ThoughtSpot Org (deploying commits into ThoughtSpot).
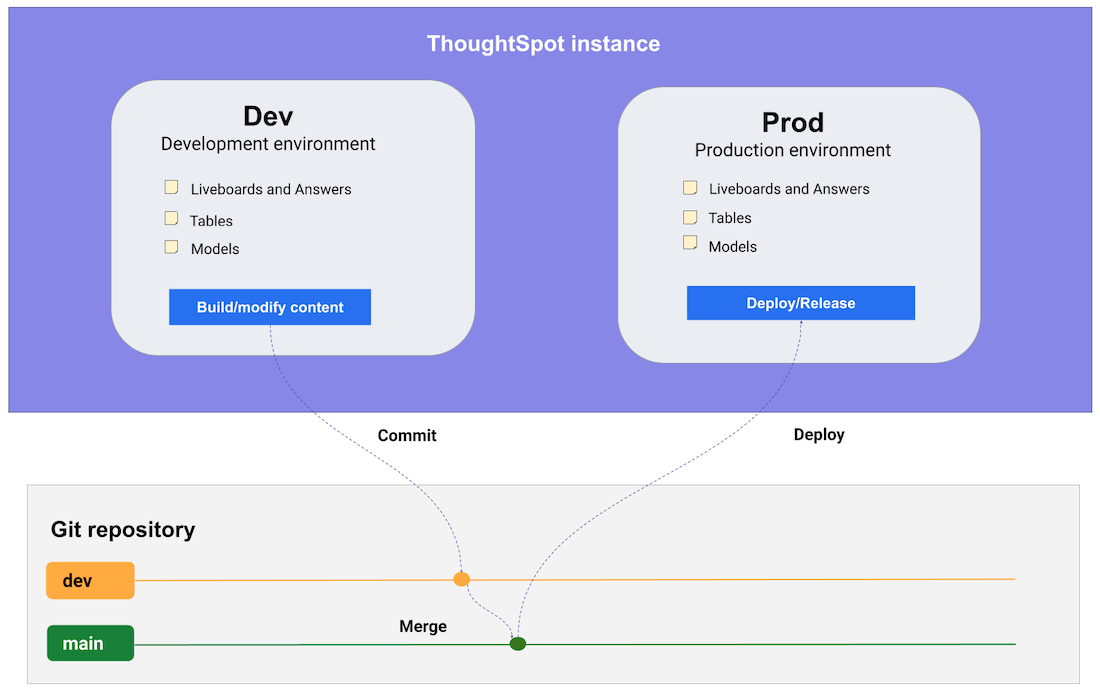
The following figure illustrates a simple Git integration workflow with ThoughtSpot Dev and Prod environments.

|
Note
|
ThoughtSpot’s Git integration does not support moving objects within the same Org. Use the TML REST APIs directly if you need to make copies with variations within a single Org. |
Moving TML changes between environments🔗
Each environment is a linked pair of a ThoughtSpot Org and a Git branch that can only export (commit) or import (deploy commits).
The standard workflow is:
-
All development work is done in the "dev environment"
-
Use /vcs/git/branches/commit (or Version Control in the UI) to commit changes to "dev branch"
-
Move changes from "dev branch" to any other environment’s branch using Git
-
Use /vsc/git/commits/deploy to deploy TML back into the desired environment’s ThoughtSpot Org
-
Set sharing, tags, custom actions, etc. for any newly created objects
|
Note
|
ThoughtSpot does not recommend committing changes to Git directly and deploying these changes back in a ThoughtSpot development environment. |
Moving changes from one branch to another🔗
Moving the changes made in commits from one Git branch to another is not handled by ThoughtSpot directly.
You must run the appropriate Git commands either via git, your software development tools, or within your Git provider’s UI. This allows your team to use Git integration with your existing Git workflows.
Typical Git processes🔗
If you are not familiar with Git, the typical process to move changes from one branch to another is called a pull request.
It is called a pull "request" because the branch with the changes is requesting they be "pulled into" the other branch, which that branch’s maintainer must approve, making choices if there are any changes that do not automatically merge.
There are many other Git commands that you can use within your own preferred processes, but creating a pull request, and then link: merging the pull request are the basic set of actions recommended by ThoughtSpot.
Deploy commits back into an environment🔗
After the pull requests are merged, the TML files in branch for the destination environment will reflect all the changes that were committed originally to the branch of the "dev" environment.
GUID mapping🔗
The deploy REST API has a GUID Mapping feature to substitute in the appropriate values for the objects on the ThoughtSpot Org.
All TML in all Git branches maintain the same GUIDs and other properties as the dev branch, while the deploy commits REST API does all necessary substitutions in the TML files prior to the final TML import action.
Validate merge before deploying🔗
Both the deploy and the validate merge APIs can be used in modes that check for errors before doing merge and deploy actions.
Sharing imported content with users and groups🔗
On the first deployment into a given Org, the objects that are newly created will not be shared with any users or groups.
The REST API for sharing objects can be called on the newly created objects. All of the GUIDs of the objects will be stored in the GUID Mapping files.
Standard content in "prod" Orgs should only ever be shared as READ-ONLY.
Recommended configuration and best practices🔗
The general practice is to use the main branch in the Git repository as the release branch, linked to the "prod" Org accessible by end customers. You are welcome to choose any branch and Org naming pattern that works for your team.
Configure connections before using deploy API🔗
Connections are the top-level object for all other ThoughtSpot objects.
At current time, do not commit TML for Connections into any branch.
Because defining a connection involves secure credentials, they are best configured manually in the UI or via a REST API script with secure access to credential details.
The simplest deployment pattern with Git is to have identical connection names across all environments, so that TML files can match on the connection name in any org.
Always use ThoughtSpot commit API🔗
As a best practice, use the commit API to submit TML changes to Git. This ensures that deleted and renamed files are properly synchronized.
One repository per ThoughtSpot project🔗
Use one repository per ThoughtSpot version control project. Your ThoughtSpot development, staging, and production environments should all be using the same Git repository. This will make it easier to move objects from dev to prod (via merging branches).
One branch per Org🔗
Use one commit branch per environment. This is where the ThoughtSpot code will get committed. Do not commit content from different ThoughtSpot environments into the same branch. Each environment uses different unique identifiers (GUIDs) to identify files. Using the same branch to store files from multiple ThoughtSpot environments will result in corrupt branches, errors, and merge conflicts when deploying content to a ThoughtSpot production environment.
Dedicated branch for configuration files🔗
Use a dedicated branch for all Git configuration files. Dedicate some branches such as dev and main for ThoughtSpot content and store all Git configuration files created by ThoughtSpot in a separate branch. This will make it much easier to compare ThoughtSpot content across branches.
Dedicated branch for version history🔗
Use a dedicated branch for version history. As described earlier, a given object’s unique identifier will be different between its development and production versions. If you wish to implement version history in a production environment, use a dedicated branch for version history. Do not use a branch that is already used to manage or deploy development objects.
Validate changes before deploying🔗
Validate the changes before merging or deploying, to ensure the TML content in target environments can import changes without conflicts.