Access control and sharing
Access control in ThoughtSpot is accomplished via sharing of content authored by one user to other users and groups.
In practice, administrators create specific access control groups to grant either read-only or edit access to content, then add users to the appropriate groups. This can be done via UI, but most often is automated via REST API or JIT provisioning during SSO.
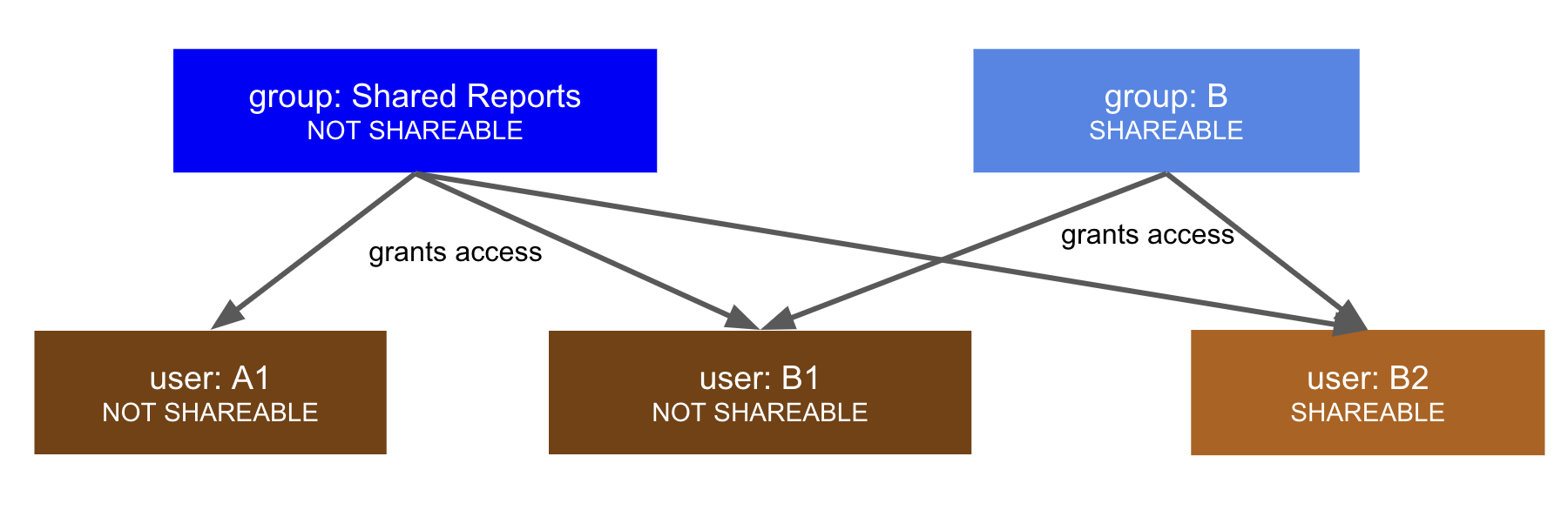
Group membership also controls which users can see each other when sharing, through a property called shareability.
|
Note
|
Avoid using the same group for access control and roles/privileges, unless all users and groups are definitely set to NOT SHAREABLE. |
Sharing model overview🔗
The user who creates content always has access to the content they are the author of.
The author of content is a single user, not a group. Authorship of content can be transferred from one user to another by an administrator account.
Users other than the author can only view and access content if it has been shared to them directly or to a group they belong to.
Group membership provides access to objects shared to the group with the permission level assigned to the group to all users who belong to the group.

Users do not see the group that provides them access to a given piece of content (the same content could be shared to multiple groups they belong to, or to them directly as well), nor do they see who shared content to them individually, although they can see the author of any content.
Sharing content🔗
ThoughtSpot users can share objects such as Liveboards, Answers, Tables, Models, and Table columns.
Sharing provides either read-only or edit permissions on an object
When an object is shared, users can view all the data regardless of the permissions set at the parent object level. For example, a user can view a shared Liveboard without having access to its underlying data source from which the visualizations in the Liveboard are built. However, there are some features of a Liveboard, which do require at least read-only permissions to the underlying data model.
Sharing visibility🔗
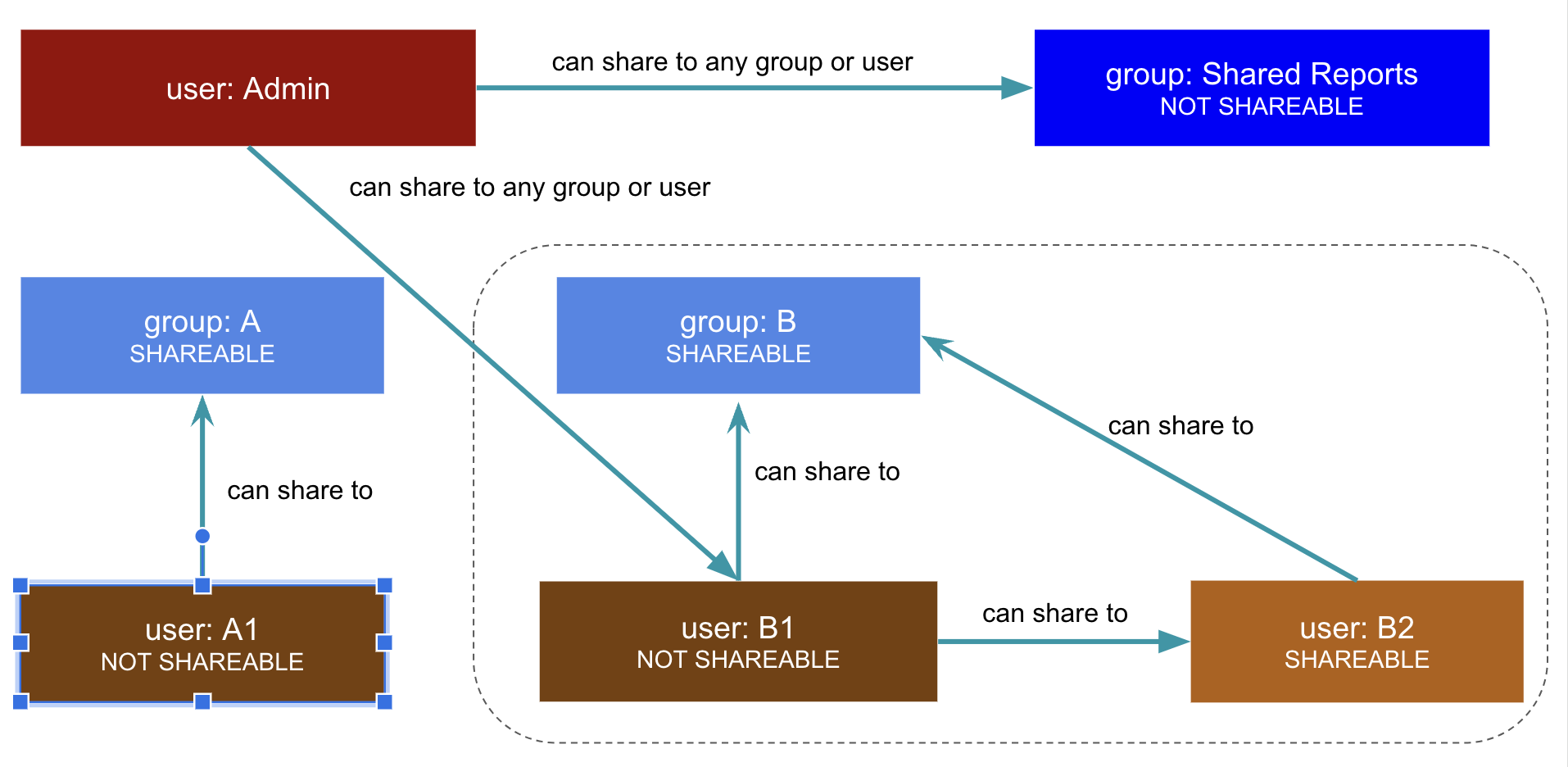
The Sharing visibility configuration allows users and groups to be set as SHAREABLE or NOT SHAREABLE.
The SHAREABLE property of a group affects the visibility of users who belong to that group. If UserA is marked as SHAREABLE, other users in the same group as UserA will see UserA in the Share dialog when they try to share an object.
A user with administrator privileges can share any content to any user or group regardless of their visibility. This allows for using a NOT SHAREABLE group as an access control group.
Sharing via UI🔗
Within the ThoughtSpot UI, there are buttons or menu items to trigger the sharing workflow for every type of object (Liveboards or Models for example).
Sharing via REST API🔗
The REST API v2 /security/metadata/share endpoint is used to programmatically share content, or to remove any access.
The API request has two components, metadata_identifiers and permissions:
-
metadata_identifiersis the list of objects being shared. -
permissionsdefines the set of users or groups (referred to as principals) being shared to, and theshare_modebeing granted. -
share_modecan be eitherREAD_ONLY,MODIFY(equivalent toEditin the UI), orNO_ACCESS.
{
"metadata_identifiers": [
"3f5d2d4b-87da-4f59-a144-85d444eada18"
],
"permissions": [
{
"principal": {
"identifier": "Group A",
"type": "USER_GROUP"
},
"share_mode": "MODIFY"
}
]
}To remove sharing to a user or group, you set their share_mode to NO_ACCESS in the request to /security/metadata/share, which effectively removes any existing share_mode granted to that user or group within ThoughtSpot:
{
"metadata_identifiers": [
"3f5d2d4b-87da-4f59-a144-85d444eada18"
],
"permissions": [
{
"principal": {
"identifier": "Group A",
"type": "USER_GROUP"
},
"share_mode": "NO_ACCESS"
}
]
}Requests to the /fetch-permissions endpoints will never return any user or group that has been set to NO_ACCESS.
Auditing access control🔗
Sharing details are not returned via the responses from the /metadata/search endpoints. Instead, there are two REST API endpoints under the /security/ for retrieving access control details.
Using the /security/metadata/fetch-permissions endpoint on an object will return the effective permissions for all groups and the users within those groups who have access to the object.
Effective permissions for an object are the full set of groups and users who have access, and what that access level is.
The /security/principals/fetch-permissions endpoint is used to get the effective permissions for a specific user or group.
Effective permissions for a user are based on things shared to them individually and their group membership. Group effective permissions should be close to their defined permissions but hierarchical groups are a feature in ThoughtSpot that would lead to more complex scenarios (hierarchical groups are discouraged when doing embedded ThoughtSpot integrations).
Re-assign content author🔗
The author of any object can be re-assigned using the V2.0 /security/metadata/assign REST API endpoint:
{
"metadata": [
{"identifier": "1ef11b25-9a95-4f03-9287-83010374962d"},
{"identifier": "3f5d2d4b-87da-4f59-a144-85d444eada18"}
],
"user_identifier": "reports_service_account_username"
}Rather than re-assigning authorship, a designated service account user is used often when importing TML objects via REST API into a different Org or ThoughtSpot instance, establishing the user used for the import process as the author within that environment.