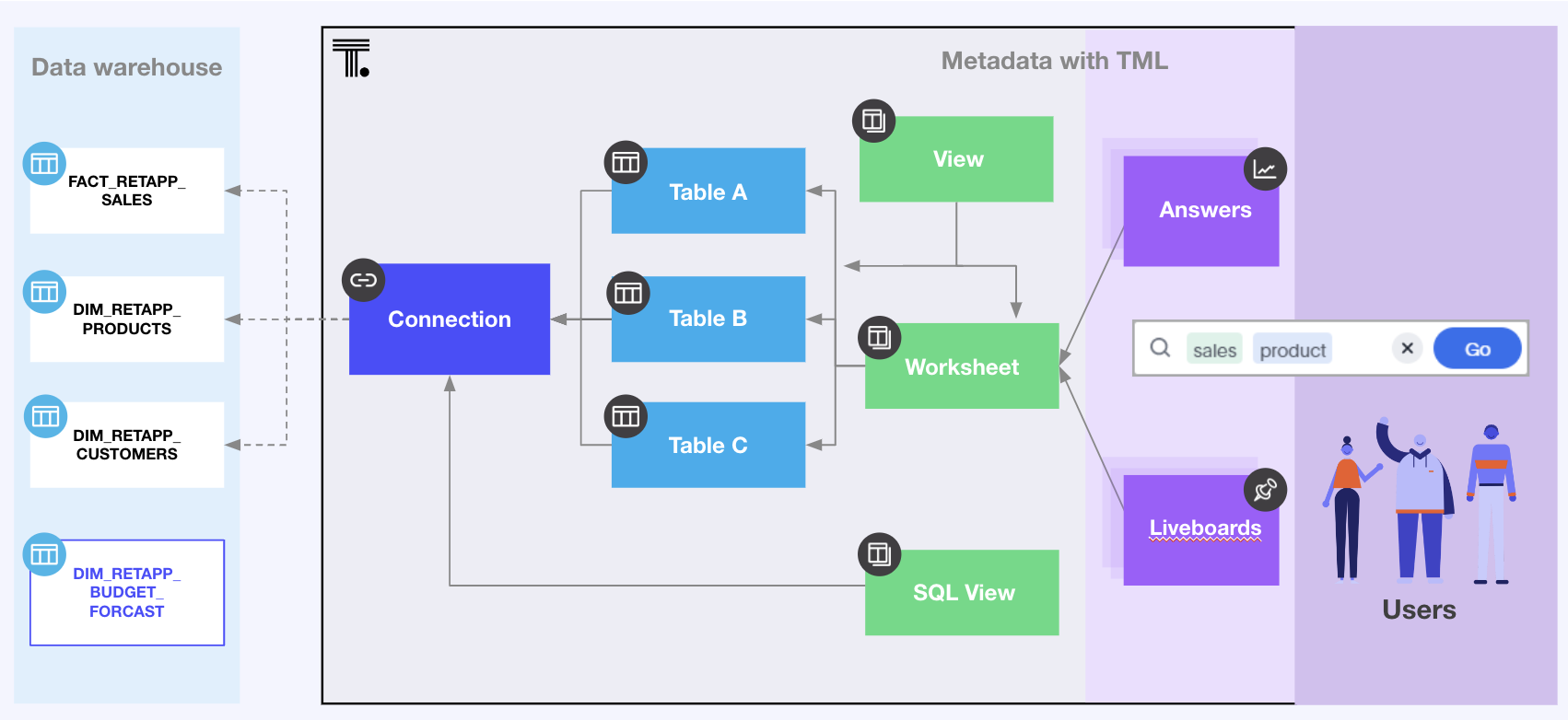
ThoughtSpot objects
ThoughtSpot is a business intelligence and data analytics platform that helps you explore, analyze and share real-time business analytics and interactive insights. Besides being an interactive data analytics platform, ThoughtSpot provides a robust and guided search functionality using which business users can search data instantly. ThoughtSpot is different from other BI tools, because ThoughtSpot Search is the core of the ThoughtSpot system.
Before you look at the rest of the developer documentation, please review this page to understand how ThoughtSpot works relative to other tools you may be familiar with.
Object model hierarchy🔗
The following figure illustrates the object model hierarchy in ThoughtSpot.

Data modeling🔗
You must create a data model comprising at least one connection with one Table to begin using Search data to create content. Most often, there will be multiple Tables, with a variety of joins defined in ThoughtSpot, with a Model bringing those tables together into a presentable analytic data model for the end-users.
Data engineers with Can manage data privilege can add connections either in the UI or via REST API. Connections are owned and accessible only to their creator, who then imports Tables from the connection. Once imported, tables can be shared with other ThoughtSpot groups and users.
Tables can have Row Level Security (RLS) rules that filter the data results based on the signed-in username or the ThoughtSpot groups to which the user belongs, and those rules apply to any Model that uses the Table.
|
Note
|
Worksheets are deprecated and replaced with Models in ThoughtSpot Cloud 10.12.0.cl and later release versions. |
Data modeling workflow🔗
-
Create a connection to a cloud data warehouse.
-
Import tables from the connection.
-
Create Models (analytic data models) based on tables. You can also create Models and add tables.
-
Create ThoughtSpot Views or SQL Views as necessary.
ThoughtSport also supports programmatic deployment of data models via ThoughtSpot Modeling Language (TML) and table import from dbt.
Content creation🔗
ThoughtSpot Search data creates a single table or chart view based on the query in the search bar and other configurations to the view made after the search results are visible.
Search data serves the role of report builder or widget designer, while Liveboards serve the role of dashboards in other tools. A single search can be saved as an Answer object, or the search result can be pinned to a Liveboard.
A Liveboard is a collection of many visualizations presented in a defined layout. You do not create the visualizations on a Liveboard directly; they are created from search data results and then pinned to a Liveboard. You can create a new Liveboard from the Liveboards page and then add a visualization from the search data result, or you can create a new Liveboard when pinning an Answer retrieved from search data.
Content creation workflow🔗
To create content:
-
Use the Search data functionality to build visualizations from data sources such as Models or Views.
-
Save the search result as an Answer or pin it to a Liveboard as a visualization.
Visualizations on a Liveboard🔗
You can add any number of visualizations retrieved from the search to a Liveboard object. Pinned visualizations exist only within the Liveboard and are independent of the objects saved as answers.
Each time you pin a search result, a separate new visualization is created on the Liveboard.
To edit a visualization on a Liveboard:
-
Go to the Liveboard.
-
Navigate to the visualization.
-
Click the More menu
 and select Edit.
and select Edit.
Visualizations on a Liveboard have their own GUIDs, but the visualization objects do not exist separately from the Liveboard object.
Tags🔗
Tags allow you to organize your objects and find them easily.
A tag object is created by the administrator, is visible to all users, and can be assigned by any user.
Tag search is always an OR operation: filtering on multiple tags results in all objects with any of the tags, not just those with all of the specified tags.
Access control (sharing)🔗
ThoughtSpot’s access control model works by an author or administrator sharing objects to ThoughtSpot groups or other individual users:
-
The creator of an object is referred to as the author.
-
The author can share the object with their groups using the Shareable property.
-
The author can share the object with other users in Shareable groups that the author belongs to, and if the other user is also marked Shareable.
An administrator user can share any object with any group or user with no restrictions. ThoughtSpot administrators can add users locally in the UI or via REST API. Similarly, they can manage groups and sharing privileges by using the Groups feature in the UI or via REST API.
Single sign-on🔗
If SAML or OpenID Connect (OIDC) integration support is enabled on your instance, users that authenticate to external identity providers (IdP) can log in to ThoughtSpot with their Single Sign-On credentials. Embedded ThoughtSpot instances also support the trusted authentication method to sign in their application users.
Object properties in REST API🔗
The object representations in ThoughtSpot REST API include the following properties:
-
id
GUID of the object. Unique within a given ThoughtSpot instance -
author
GUID of the user who created / uploaded the object, or had the object transferred to them. -
owner
GUID representing the relationship between hierarchical objects, For example, a column would have the GUID of a Table or Model as owner. -
created
timestamp of object creation -
modified
timestamp from last time object was modified -
modifiedBy
GUID of the user who last modified the object -
tags
An array of tag objects representing the tags assigned to the object.
Object names in REST API v1🔗
The object type names in the ThoughtSpot REST API v1 differ from the current names seen in the ThoughtSpot UI. Data objects have both a type and a subtypes within the REST API, allowing you to request all valid data objects or specify the individual subtype.
The following notation is used in REST API v1 for object types:
-
Answers:
QUESTION_ANSWER_BOOK -
Liveboards:
PINBOARD_ANSWER_BOOK -
Connections:
DATA_SOURCE -
Data objects:
LOGICAL_TABLE, with the following subtypes:-
Tables:
ONE_TO_ONE_LOGICAL -
Models:
WORKSHEET -
Views:
AGGR_WORKSHEET -
SQL views:
SQL_VIEW -
CSV imported data:
USER_DEFINED
-
-
Joins:
LOGICAL_RELATIONSHIP -
Columns:
LOGICAL_COLUMN -
Tags:
TAG -
Users:
USER -
Groups:
USER_GROUP
Column and join objects with their own GUIDs do exist within the ThoughtSpot system, but they are connected to Tables, Models, or other data objects. Columns and joins can be viewed or modified only within the context of the data object to which they belong.