Security setup
ThoughtSpot Embedded applications operate securely with ThoughtSpot. This lesson will walk you through the security setup required for embedding ThoughtSpot.
Pre-conditions🔗
-
You should have completed Setting up for the course.
-
Your account must have administration privileges to configure security settings.
-
If you are using an Orgs-enabled instance of ThoughtSpot, familiarize yourself with Orgs settings, because some settings are set at the Primary-Org level. This lesson will show the instance-level settings.
Types of security🔗
Security is applied to web applications in many ways. In the case of ThoughtSpot Embedded, there are some settings specific to embedding, and a few for the ThoughtSpot application. This tutorial focuses on the settings that are specific to ThoughtSpot Embedded, but we’ll describe all types before getting into the details.
Security when using ThoughtSpot and ThoughtSpot Embedded can be in the following buckets that work together to apply end-to-end content and data security. Each type of security is identified here with information about where the security is managed.
| Security setting | Managed at |
|---|---|
Embed / web security are the security settings that allow you to embed ThoughtSpot into your application | ThoughtSpot Embedded |
Authentication determines how you will authenticate the user with ThoughtSpot. Both the authentication supported by ThoughtSpot and ThoughtSpot Embedded have to be considered. | ThoughtSpot Embedded |
Content security is managed by ThoughtSpot to determine what content a user has access to, such as Tables, Models (formerly Worksheets), and Liveboards. Data security can be controlled separately | ThoughtSpot Analytics application. For more information, see the following sections. |
System privileges / roles define what a user can do inside ThoughtSpot, such as downloading data or using SpotIQ. | ThoughtSpot Analytics application |
Data security restricts the columns or rows of data from the source data. Data security is managed via row-level security settings or column sharing in ThoughtSpot. It can also be controlled using pass-through security to the Cloud data warehouse. | ThoughtSpot Analytics application |
Embed / web security🔗
The embed and web security settings determine which applications can embed ThoughtSpot and make API calls via JavaScript (cross-site scripting).
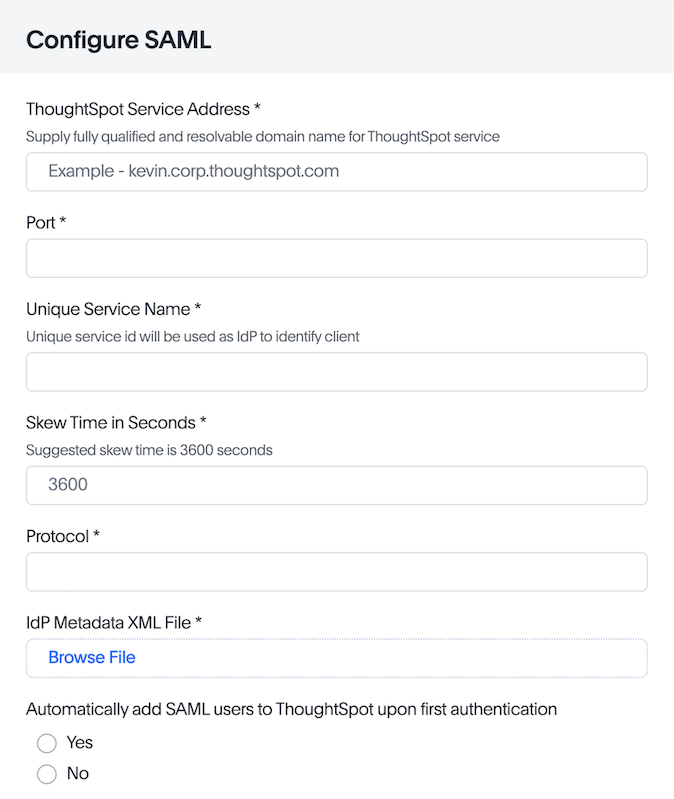
Security settings are set on the Developer > Customisations > Security Settings page in the ThoughtSpot UI. You can see this page if you have Developer or Administrator privileges. To configure the settings, you will need administrator privileges.
The following are the most important settings for embedding ThoughtSpot. Except for very simple embedding scenarios, all of these are typically set for the URL of the ThoughtSpot Embedded application embedding ThoughtSpot components.
CSP visual embed hosts🔗
CSP visual embed hosts are the URLs that are permitted to embed ThoughtSpot. For example, https://mycoolapp.mycompany.com. If your app URL is not in the list, then you will get CSP errors when embedding. For development, you can add localhost, but it’s not recommended for production environments. You only need a port if you are using a non-standard port such as 80, 443.
CSP connect-src domains🔗
The CSP connect-src domains are those domains that you can send data to. This is mostly used for custom actions, including both callback and URL actions. This setting has the same constraints as the CSP visual embed hosts. Failure to set this setting can also result in CSP errors.
CORS trusted domains🔗
Domains added to CORS allowlist can use cross-site scripting, that is, calling web service endpoints (including login) from a web application. Command-line applications and tools, such as CURL, are not impacted by this setting. The values are the list of domains (without protocol) and any non-standard ports, such as 8080. If CORS isn’t set, you will see CORS errors in the console log for web service calls.
You will need to add the CORS setting either in your system or the trial instance. Add localhost:8000 if that’s your URL. Note that 127.0.0.1 is not the same, so if you are using an IP, set that instead.
For more details, see the security setting documentation, which also includes constraints on values for the above settings.
Authentication🔗
Authentication is how users are identified, given access, and logged in to ThoughtSpot. Before a user can be authenticated, they have to exist in the ThoughtSpot system, and they are usually assigned to some groups. Typically, this assignment is a separate process, but it is possible if using SAML to create the user and assign them to groups when doing the initial authentication. Other alternatives include manually creating users and using the APIs to create users and groups. The creation of users and groups is not covered in this course.
The following table lists the types of authentication, the associated enumerated type in the SDK, and if the users can be created on demand. Don’t worry about the AuthType right now, but it will be used later when initializing the SDK.
| Type | AuthType | Description | Can Create? |
|---|---|---|---|
No Authentication | AuthType.None | No authentication by the SDK | No |
Basic | AuthType.Basic | Username / Password | No |
SSO with iframe redirect | AuthType.EmbeddedSSO | SSO or OIDC when iframe redirect is supported by the IdP. | No |
AuthType.SAMLRedirect | SSO with SAML | Yes | |
AuthType.OIDCRedirect | SSO with Open ID Connect | No | |
Trusted Authentication | AuthType.AuthServer | ThoughtSpot token-based approach | Yes |
Each of these approaches is explored in detail in the following sections.
No authentication🔗
No Authentication (AuthType.None) is exactly what it sounds like. The user is not authenticated to ThoughtSpot. If the user isn’t logged into ThoughtSpot, the embedded content will display a login page for the user to log in. This authentication type is used only during development. However, if you are logged into ThoughtSpot in another tab or browser window, you will be authenticated already.
Basic authentication🔗
Basic authentication is traditional username and password authentication. This approach is typically only used in development or test, but can also be used in your webapp if you prompt the user for the login info. You don’t want to put a username and password in your code because then it can be seen by viewing the source.
EmbeddedSSO authentication🔗
The EmbeddedSSO authentication supports both SAML 2.0 and OpenID authentication when the identity provider supports iframe redirect. Most modern IdPs support iframe redirect, so if you are using SAML or OIDC, this is the type you most likely want to use. If iframe redirect is not supported, you can use one of the following.
SAML authentication🔗
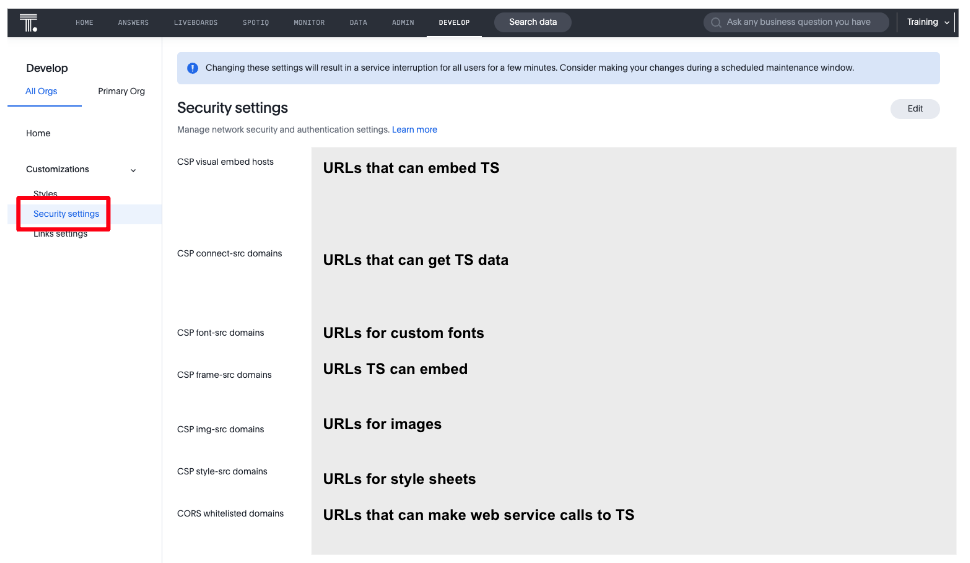
SAML authentication uses SAML 2.0 to authenticate the user. With this approach, ThoughtSpot is set up within a federation using an Identity Provider (IdP), such as Okta or something similar. When the user attempts to view ThoughtSpot content, ThoughtSpot will make a check to the IdP to verify the user is authenticated. Usually, the embedding application is also part of the same federation, so the user is already authenticated. It’s not required, but if the user isn’t authenticated, they will have to authenticate with the IdP.
SAML configuration requires Administrator privileges in ThoughtSpot. It shows up in the Admin page of the UI. You will need to provide information about the IdP, including uploading a metadata XML file. For more information, see SAML SSO documentation. The IdP will also have to be set up to match the ThoughtSpot configuration. See the IdP’s documentation on how to set it up.

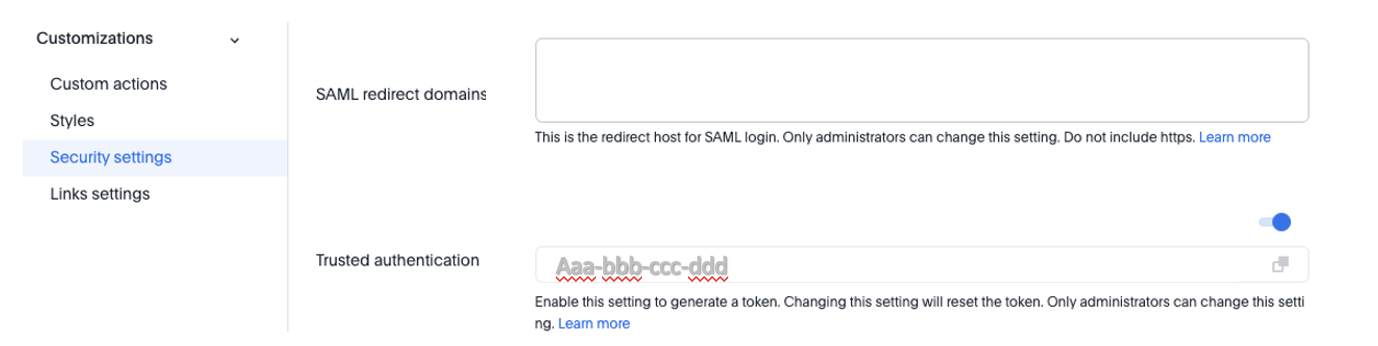
Once you have the SAML federation set up for ThoughtSpot, you also have to enable the SAML redirect for the authentication. This is set from the Developer | Security Settings. If this value is not set, then you will get errors trying to redirect back to your application.
See the SAML SSO documentation for more details.
OIDC authentication🔗
OIDC (Open ID Connect) is a newer standard based on OAuth 2.0. This auth type has been added more recently (2022) as a supported type. OIDC configuration is not currently supported in the UI, so you will need to work with the ThoughtSpot support team to configure OIDC.
See the documentation for more details on using OIDC.
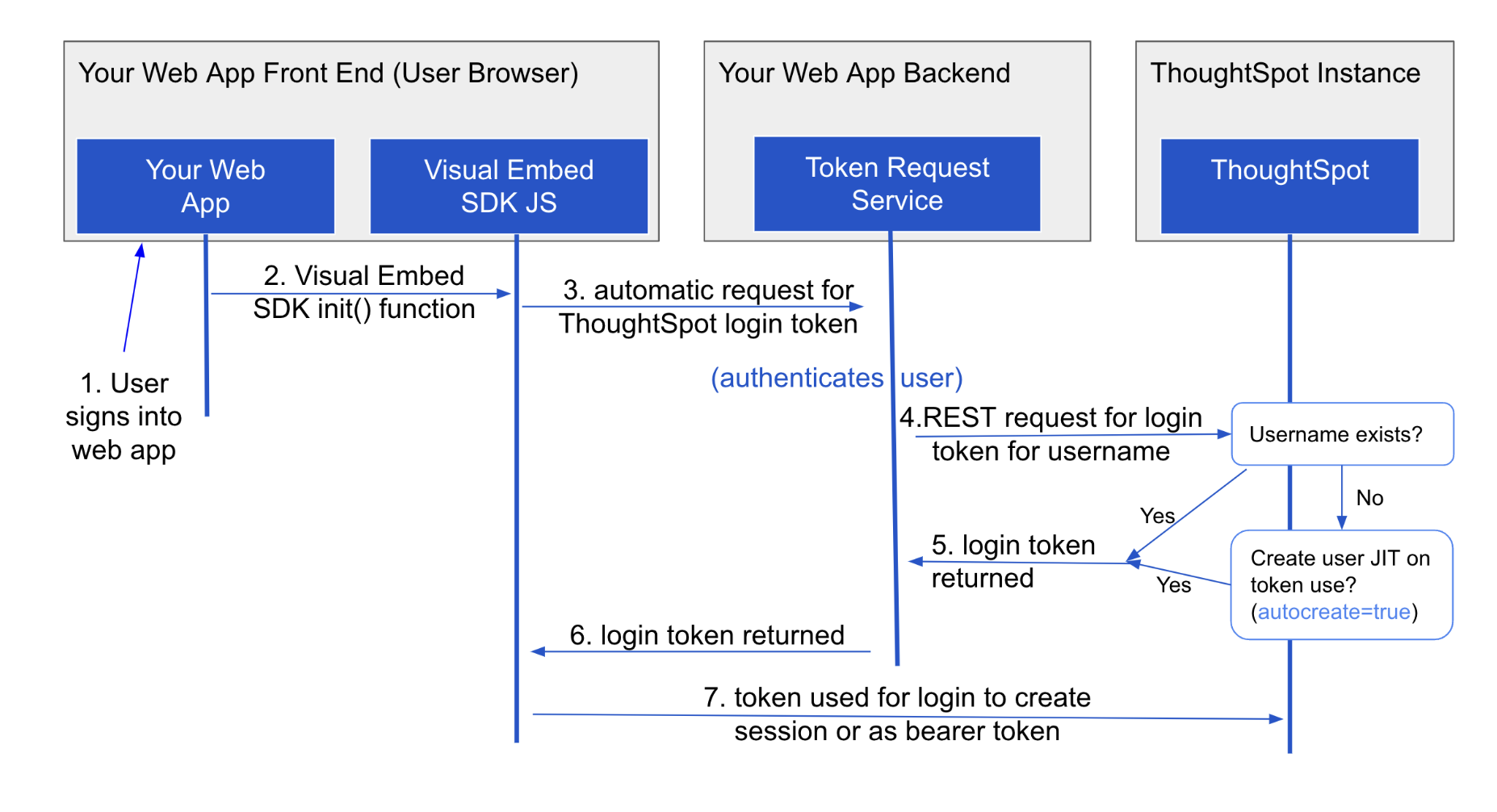
Trusted authentication🔗
Trusted authentication is a ThoughtSpot specific approach to authentication that is typically used when other SSO scenarios such as SAML or OIDC, aren’t being used. Trusted Authentication is only used with ThoughtSpot Embedded (including REST API calls). With Trusted Authentication, you use a separate server that will authenticate on behalf of the user with a secret token. This token is then used by the user to authenticate with ThoughtSpot. If the user doesn’t exist, it can be created as part of the call to get a token from ThoughtSpot.

To enable trusted authentication you have to navigate to the Developer | Security Settings page and enable it via the toggle switch. Note that only an administrator can make this change. Once enabled, you will get a cluster wide key that you can copy and use in API calls. KEEP THIS KEY PRIVATE! It is a cluster wide key that allows you to create sessions on behalf of any user.
|
Note
| On instances with Orgs enabled, you can also enable trusted authentication at the org level in addition to the instance level. The token created can only be used to log into the given org. |
See the documentation for more details about Trusted Authentication.
Activities🔗
-
Review the Security settings documentation.
-
Review the documentation for authentication SAML SSO, OIDC, Trusted Authentication.
-
Set the appropriate settings for your environment unless you are using the ThoughtSpot trial instance.