Trusted authentication
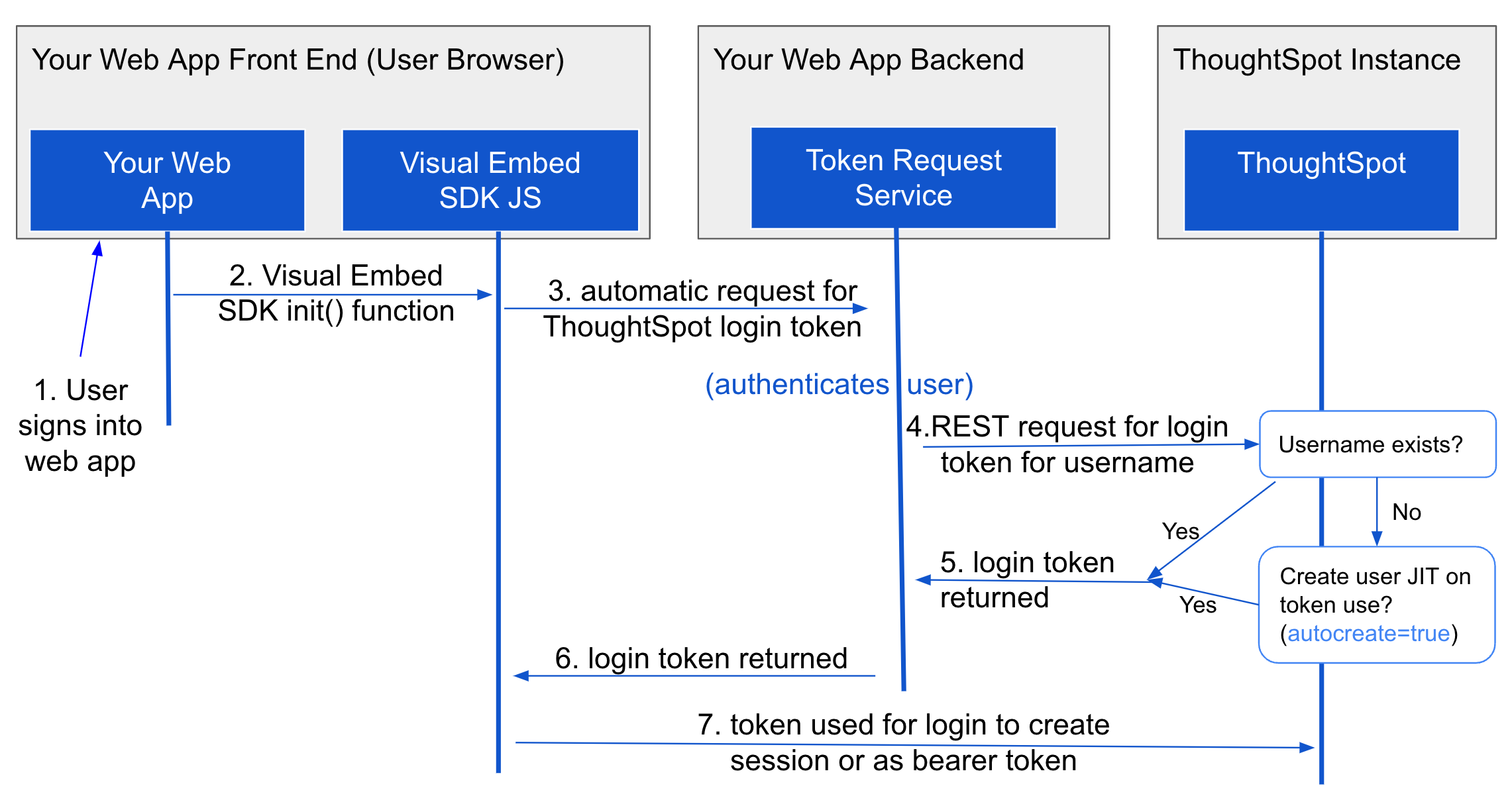
Trusted authentication allows a web application to authenticate a user to a ThoughtSpot instance using login tokens requested from a ThoughtSpot instance.
It is the most seamless method of single sign-on (SSO) available to embed ThoughtSpot, but the actual authentication of the user is performed only by the web application, which then securely passes the user details to a token request service that must be developed and added to the web application.
Trusted authentication can also be used for back-end REST API processes that need to impersonate an individual user to retrieve a filtered data response. In those scenarios, you implement the token retrieval and sign-in calls directly without the browser portion.

Overview of implementation🔗
The trusted authentication implementation method includes the following steps:
-
Enable Trusted authentication on ThoughtSpot in the Develop > Customizations > Security Settings page. Copy the
secret_keyand place where the token request service can securely access it. -
Create the token request service, typically a REST API endpoint in the embedding application. This service returns a login token for the user signed in by the web application.
-
Include the Visual Embed SDK into the embedding web application. The authentication type is defined in the
initfunction. You can configure cookie-based (AuthType.TrustedAuthToken) or cookieless authentication (AuthType.TrustedAuthTokenCookieless) as per your deployment needs. -
When
init()is called, the SDK checks if there is an existing ThoughtSpot session for the instance in the browser. If not, it will request a login token from either theauthEndpointURL specified in the SDK or thegetAuthTokencallback function. ForauthEndPoint, specify the authentication endpoint URL from which you want to obtain the authentication token. If usinggetAuthToken, call thegetAuthTokenfunction to invoke your login endpoint. The login endpoint then returns aPromisestring that resolves to an authentication token.
Cookie-based vs cookieless authentication🔗
The trusted authentication method supports cookie-based and cookieless authentication.
In cookie-based authentication, the login token is only necessary during the login process, after which any request to ThoughtSpot will include session cookies that identify the signed-in user.
In cookieless authentication, the bearer token issued by the authentication server is used to authenticate API requests to ThoughtSpot.
If you are embedding ThoughtSpot content in an app that is not in the same domain as your ThoughtSpot instance, and your web browser blocks third-party cookies, use cookieless authentication.
See the Visual Embed SDK documentation for the exact details of implementing either form of trusted authentication.
How to turn off trusted authentication🔗
Disabling trusted authentication also invalidates the previous secret_key.
Troubleshoot trusted authentication🔗
Please see the troubleshooting steps if you encounter issues with the browser-side aspects of the trusted authentication implementation.
Trusted authentication code samples🔗
Code examples for implementations of a token request service are available here.
Examples of front-end JavaScript for trusted authentication using the Visual Embed SDK are documented here.
The sample code of an application frontend authenticating via trusted authentication is available on the GitHub repository and the React components code sandbox.
REST API back-end use cases🔗
With access to the secret_key, back-end REST API processes can request a token for any user, and then use the returned token as:
-
a login token using
session/loginto create a long-lived session as that user -
a bearer token for all subsequent REST API calls
Additional resources🔗
-
Big React Demo
The React demo shows how to implement trusted authentication as part of an application integrated with various ThoughtSpot components -
Python REST API library
A library implementing the V1 and V2 REST APIs in Python