
OpenID Connect authentication
OpenID Connect (OIDC) is an authentication protocol that adds an identity layer to the OAuth 2.0 protocol. OIDC allows clients to verify a user’s identity based on the authentication performed by an authorization server. Using the OIDC authentication framework, end users can access multiple applications, websites using their single sign-on credentials.
To get familiar with the common OIDC terminologies, see the following page OIDC concepts and terms.
OIDC authentication workflow🔗
The following figure illustrates the OIDC authentication workflow for an embedded ThoughtSpot instance:

The OIDC authentication workflow involves the following steps:
-
A user logs into the host application and requests access to the embedded ThoughtSpot content.
-
The SDK checks for an existing user session in the browser.
-
If there is no session, it sends a
GETrequest to the OpenID authorization endpoint configured on ThoughtSpot to obtain an authorization code. -
The OpenID authorization server returns an authorization code.
-
The SDK sends the authorization code with the ThoughtSpot client credentials in a
POSTrequest to the OpenID token endpoint. -
The token endpoint returns an ID and access token in exchange for the authorization code.
-
The SDK validates the ID token and authenticates the user.
-
If the authentication is successful, the web browser redirects the user to the requested page.
OIDC configuration steps🔗
ThoughtSpot supports the Authorization code flow in which an authorization server at the OpenID provider’s end verifies the identity of a ThoughtSpot user and grants authorization code and tokens. This method of authentication and authorization requires ThoughtSpot to obtain authorization code, ID and access tokens, and validate these tokens before granting access to its resource.
The OIDC configuration procedure includes the following steps:
-
Register your ThoughtSpot instance and the redirect URI in the OpenID provider
-
Enable OIDC authentication support on ThoughtSpot with IAMv1 (Requires assistance from ThoughtSpot Support)
-
Enable OIDC authentication support on ThoughtSpot with IAMv2 (Requires assistance from ThoughtSpot Support)
-
Enable OIDC authentication in the Visual Embed SDK (For embedded ThoughtSpot instances only)
Register ThoughtSpot and set the redirect URI🔗
To register the ThoughtSpot as a client in the OpenID provider server, see the following page Register ThoughtSpot and set the redirect URI.
After you register ThoughtSpot as a relying party and set the redirect URI, the OpenID provider provides the following information:
- Client ID
-
The
client_idstring. - Client secret
-
The
client_secretstring. - Issuer
-
The OpenID provider URL from which ThoughtSpot can discover the OpenID provider metadata, such as the authorization, token, user information, and public-keys endpoints, and supported scope and claims.
- Redirect URI
-
The registered redirect URI to which the authorization response will be sent.
Enable OIDC authentication support on ThoughtSpot with IAMv1🔗
|
Note
|
You must contact ThoughtSpot Support to enable OIDC authentication support on ThoughtSpot. |
To configure ThoughtSpot for OpenID Connect authentication, the following attributes and metadata are required.
- Client ID and client secret
-
The OpenID provider generates a
client_idandclient_secretafter you successfully register ThoughtSpot as a relying party. Theclient_idandclient_secretare required parameters in theGETandPOSTrequests sent by ThoughtSpot to the authorization and token endpoints. - Authorization, token, and user information endpoints
-
For the user authentication process, ThoughtSpot will require the URIs of the authorization, token, and user information endpoints. ThoughtSpot can retrieve this information dynamically from the issuer URL using the
/.well-known/openid-configurationendpoint. You can obtain the issuer URL after registering ThoughtSpot as a client in the OpenID provider system.https://<issuer-url>/.well-known/openid-configuration
-
Supported scopes
You can obtain the scope that your OpenID provider supports from the OpenID provider metadata.
The following scopes are mandatory for OIDC configuration on ThoughtSpot. ThoughtSpot sends the
scopeattributes in theGETrequest to the OpenID authorization endpoint.-
openidAll OpenID Connect requests must contain the
openidscope value. -
profileIf the
profilescope value is present, the ID token will include the user’s default profile claims. -
emailIf the
emailscope value is present, the ID token includesemailandemail_verifiedclaims.
-
-
Supported claims
Claims that your OpenID provider uses. During ID token validation, ThoughtSpot verifies the tokens for the following claims:
-
issThe issuer ID of the OpenID provider.
-
audAudience or the intended recipient. This claim must contain the client ID issued for ThoughtSpot by the OpenID provider.
-
expThe expiration time for validating the token.
To update the user profile on the ThoughtSpot cluster, the ID token claims must include the following properties:
-
-
preferred_usernamePreferred username of the user. It maps to the
usernameattribute in the user profile on ThoughtSpot. To include this claim in the ID token, thescopeattribute must be set toprofilein the authentication request sent to the authorization endpoint. -
displayNameThe display name of the user. It maps to the
displayNameattribute in the user profile on ThoughtSpot. The default value is derived from thenameclaim. -
emailEmail address of the user. It maps to the
mailattribute in the user profile on ThoughtSpot. To include this claim in the ID token, thescopeattribute must be set toemailin the authentication request sent to the authorization endpoint. -
sub
The unique ID issued for the user at the OpenID provider. Maps to
oktauseridattribute on ThoughtSpot. -
For detailed information on enabling OIDC authentication on your ThoughtSpot instance with IAMv1, see the page Enable OIDC authentication.
Enable OIDC authentication support on ThoughtSpot with IAMv2🔗
|
Note
|
You need admin privileges to enable OIDC authentication with IAMv2 on ThoughtSpot. |
With OIDC, users can authenticate to the identity provider (IdP) to access the ThoughtSpot application, or the embedded ThoughtSpot content in an external web application. With IAMv2, ThoughtSpot powers its internal authentication with Okta. IAMv2 involves several external improvements to authentication, including security enhancements.
To enable OIDC authentication on ThoughtSpot using IAMv2, navigate to the Authentication section in the Admin panel, and click Single Sign On. Select the OIDC IDP and enter the following IdP details:
- Connection name
-
Provide a name for the configuration of the connection to your identity provider, helping to distinguish and manage multiple connections. This appears as the connection name on the Admin Console.
- Client Secret
-
Enter the Client Secret associated with the Client ID for secure communication.
- Client Id
-
A public identifier for the client, is used by the authorization server to recognize and validate the client. Enter the Client ID provided by the OIDC IdP when you registered your application.
- Scopes
-
The specific permissions or access levels granted by the user during the authentication process. This defines the extent of data and actions the client can perform. You can obtain the scope that your OpenID provider supports from the OpenID provider metadata.
The following scopes are mandatory for OIDC configuration on ThoughtSpot. ThoughtSpot sends the
scopeattributes in theGETrequest to the OpenID authorization endpoint.-
openidAll OpenID Connect requests must contain the openid scope value. -
profileIf the profile scope value is present, the ID token will include the user’s default profile claims. -
emailIf the email scope value is present, the ID token includes email and email-verified claims.
-
- Authorization Endpoint
-
URL where the OpenID provider initiates the authorization process by redirecting the user’s browser to this endpoint for authentication.
- Token Endpoint
-
URL where the OpenID provider endpoint returns an ID and access token in exchange for an authorization code. ThoughtSpot sends the authorization code obtained from the authorization server to the token endpoint to obtain an ID and access token.
- Issuer
-
Typically represented as a URL which represents the unique identifier for the OpenID Connect provider serving as a trusted endpoint for authentication.
- User Info Endpoint
-
Optional. URL for retrieving additional user information after authentication, providing user details.
- Jwks (JSON Web Key Set) Endpoint
-
URL for obtaining a JSON Web Key Set, used to verify the authenticity of tokens issued by the IdP.
- Auto create user (JIT)
-
This toggle allows you to specify whether user accounts should be created automatically upon their first authentication if they don’t already exist. When enabled, it streamlines the user creation process.
The IdP details will have to be mapped with these ThoughtSpot attributes:
- Username
-
ThoughtSpot username corresponding to the username from the IdP.
-
ThoughtSpot email associated with the email of the user in the IdP.
- Display name
-
Optional. The display name for the user.
- roles
-
Optional. Roles associated with the user. This mapping is crucial for assigning the correct roles and permissions to users based on their authentication through OIDC.
For detailed information on enabling OIDC authentication on your ThoughtSpot instance using IAMv2, and attributes, see Enable OIDC authentication.
Enable OIDC authentication in the Visual Embed SDK🔗
To enable OIDC authentication support on an embedded ThoughtSpot instance, make sure you set the AuthType parameter to OIDCRedirect in the SDK when calling the init function from your application.
init({
thoughtSpotHost: "https://<hostname>:<port>",
authType: AuthType.OIDCRedirect,
});Org mapping with OIDC assertion🔗
|
Note
|
|
With Org mapping, the IdP will have the ability to authenticate and log in OIDC users in ThoughtSpot. IdP will have to send a list of the Org names and the user will be assigned to these Orgs. By default, the Org mapping is disabled on the ThoughtSpot instance. To enable it in the Admin panel of the ThoughSpot instance, follow these steps:
-
Ensure Orgs are enabled for your ThoughtSpot cluster.
-
Enable JIT user creation to automatically create user accounts if they don’t exist in ThoughtSpot during authentication.
-
Configure the OIDC assertion on IdP side. This assertion will be sent as a part of the ID Token.The following screenshot shows a sample configuration on Okta.
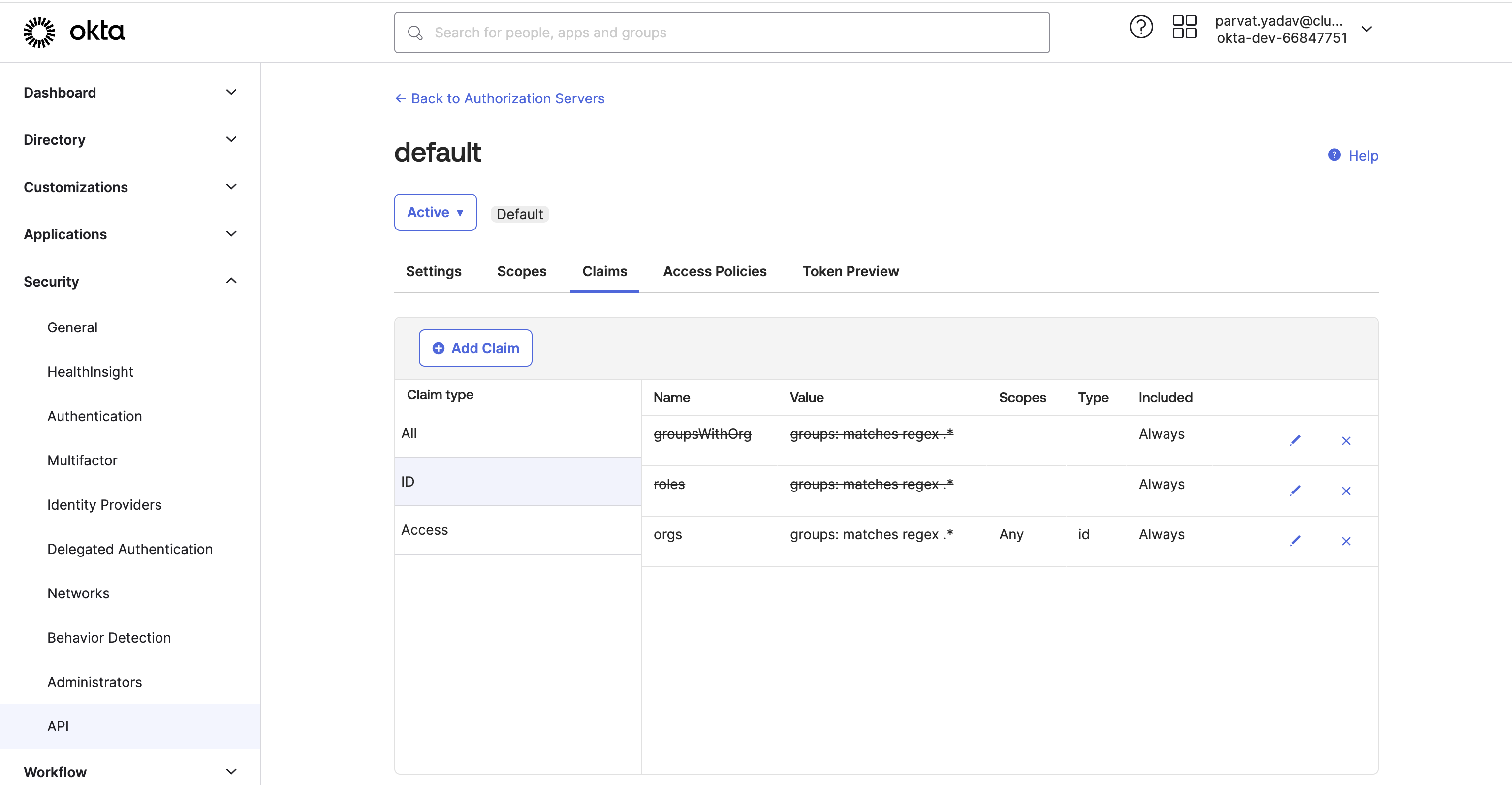
-
Ensure the mapping attributes are configured on your ThoughtSpot instance.
Group synchronization🔗
The group synchronization feature reads the Group claim from the ID token provided by the OpenID provider and creates groups in ThoughtSpot. To enable group synchronization on ThoughtSpot, contact ThoughtSpot Support.
|
Note
|
If a group is deleted from the OpenID provider server, the corresponding group in ThoughtSpot will not be deleted during group synchronization. You must manually delete it in ThoughtSpot. |