<div id="div-nav-links">
<ul id="ul-nav-links">
<li id="search-link">Search</li> <!-- lesson 05 -->
<li>|</li>
<li id="sage-link">Natural Language</li> <!-- lesson 06 -->
</ul>
</div>Embed Natural Language Search
Now that you’ve embedded a search, you’ll notice that the rest of the embedding follows the same basic pattern:
-
Create the component in the Playground.
-
Add the component to your code and render it.
In this lesson, we’ll embed Natural Language Search components into the application.
Add a nav link and function for the natural language search🔗
First, add a nav link for the natural language embed. In the index.html file, add a new <li> for the natural language search page. We’ll also add a pipe character | as a separator in the menu. Your code should look like this:
Now run the application to verify everything is working. You should see the Search and Natural Language links in the menu.

Add a listener for the search link🔗
In tse.js, add the following line of code to register a listener for the click event. When clicked, it will call the onSage function. Place this after the listener added in the previous lesson. The event listener section should now have two listeners.
document.getElementById("search-link").addEventListener("click", onSearch);
document.getElementById("sage-link").addEventListener("click", onSage);Next, add the onSage function. Initially, this will just log a message to the console to confirm it’s being triggered.
const onSage = () => {
console.log('using natural language search');
}Refresh the application and click the Natural Language link. You should see the console log message in the developer tools. If not, check for errors.
Generate a natural language search to embed🔗
If you’re not already in the Visual SDK playground, navigate there and select Natural Language Search from the dropdown menu. You should see an empty page with the Natural Language Search bar as shown here:
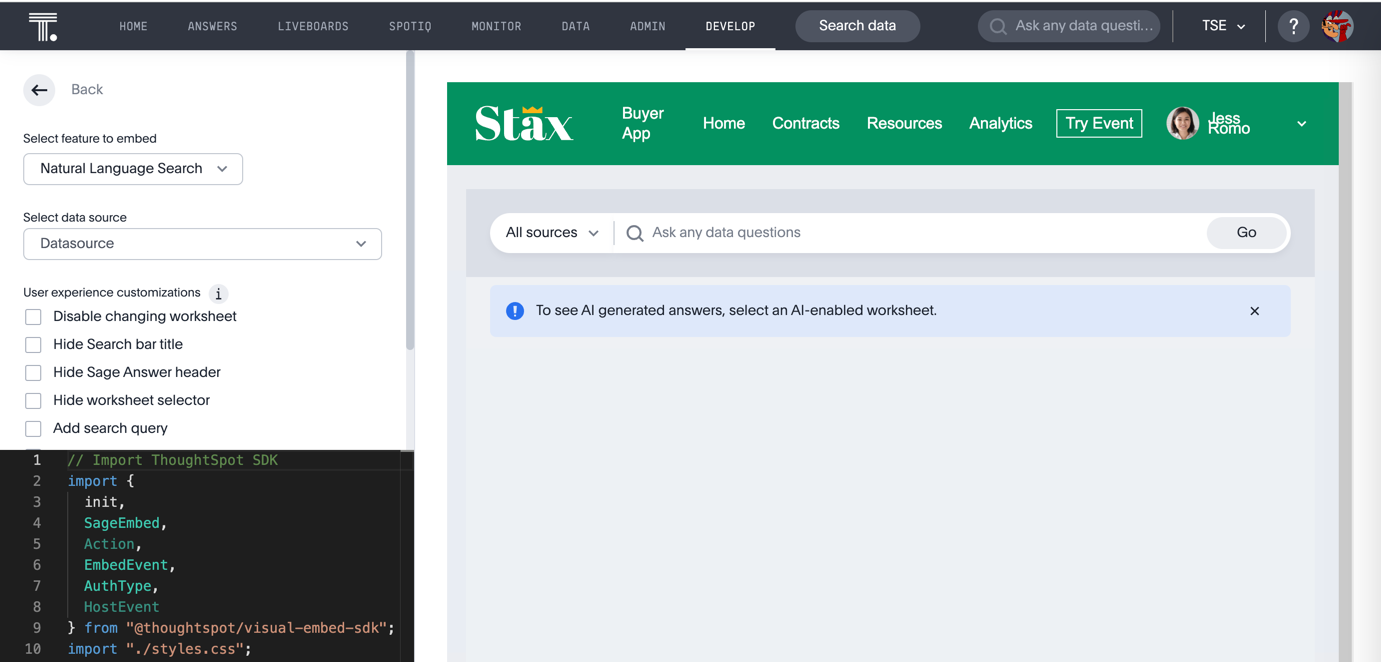
Let’s review the SageEmbed-specific settings and configure the embed.
-
The
Select data sourcedropdown is similar to what we used for the Search embed. It will display any Models enabled for natural language search. Select one from the dropdown to update the code with the data source’s GUID.
Unlike the Search embed, you can only have one data source for natural language search, and a data source is always required for natural language search, though it can be user-provided.
Now, set some additional options:
-
Disable changing model: Prevents the user from changing the pre-selected data source.
-
Hide Sage Answer header: Hides the "AI answer" header in the results.
-
Add search query: Predefines a text query to run automatically, similar to the search embed.
For this exercise, select the options Disable changing model, Hide Sage Answer header, and Add search query. Enter a search query, then press Run. You should see a result like this:
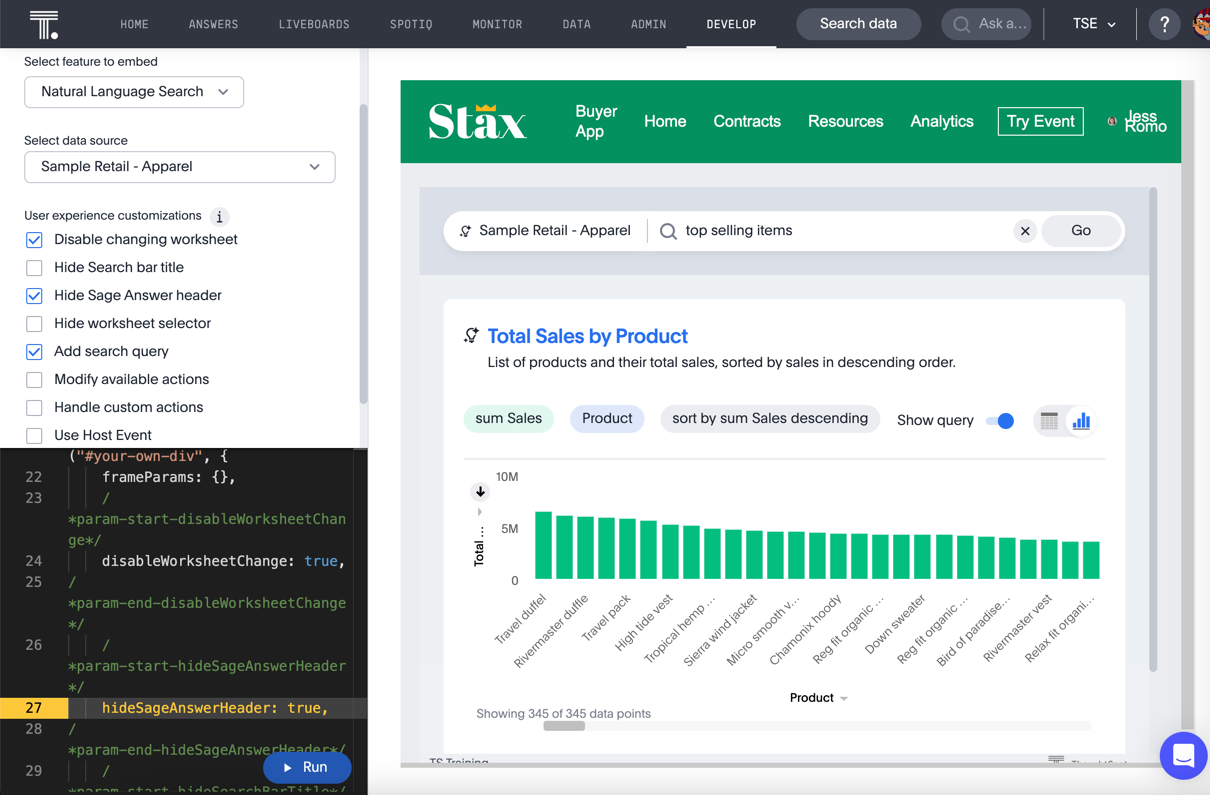
Embed the natural language search into the application🔗
Now that we’ve created the natural language embed component using the playground, let’s add it to the onSage function. Remember to update the div ID from #your-own-div to #embed to match the index.html file. Finally, add a call to render().
Here is the resulting function with comments removed and the DIV ID updated:
const onSage = () => {
const embed = new SageEmbed("#embed", {
frameParams: {},
disableWorksheetChange: true,
hideSageAnswerHeader: true,
dataSource: "4d98d3f5-5c6a-44eb-82fb-d529ca20e31f", // Your data source ID
searchOptions: {
searchQuery: "top selling items",
executeSearch: true,
},
});
embed.render();
};Test natural language search embed🔗
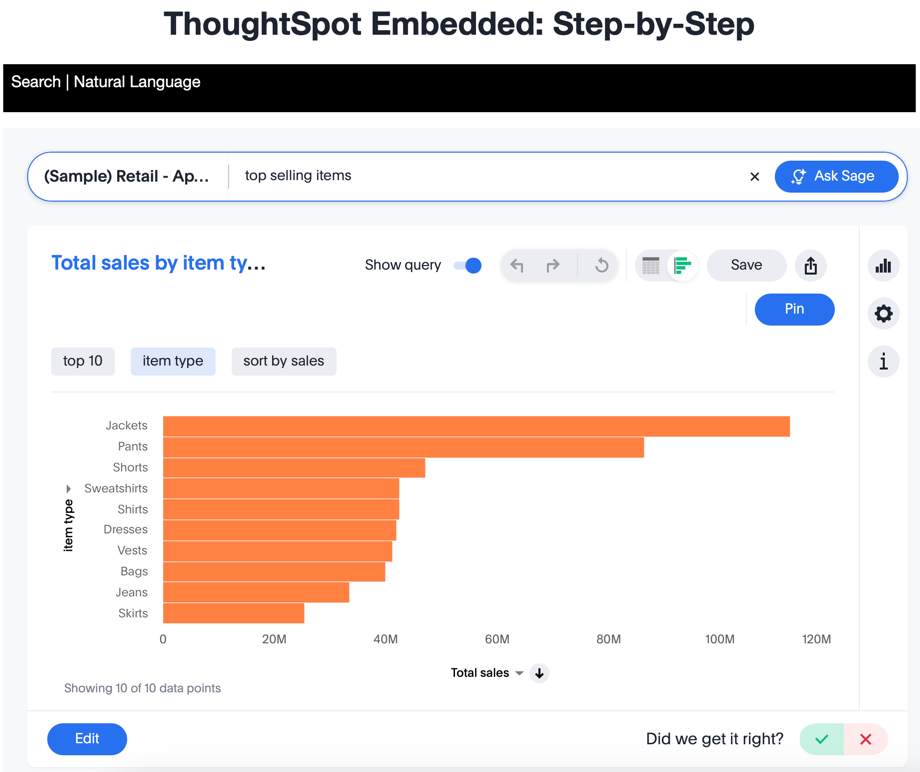
The final step is to test the Sage embed. Refresh the application (with cache disabled), then click the Sage link. You should see something like this:
Activities🔗
-
Add the nav link and handler to your code.
-
Import
SageEmbed. -
Use the playground to create a natural language search embed component.
-
Copy the search embed component from the playground to your code and modify the DIV ID.
-
Add a
render()call. -
Test the code.
If you run into issues, you can reference the code in the src folder.