MCP server integration
ThoughtSpot’s Agentic Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server allows you to integrate ThoughtSpot analytics directly into any AI agent, custom chatbot, or LLM-based platforms that support MCP. It acts as a connector between the ThoughtSpot instance and external AI client, and provides a set of tools for interacting with ThoughtSpot’s data and its analytics capabilities programmatically.
The ThoughtSpot MCP Server is an add-on feature available with the ThoughtSpot Analytics and ThoughtSpot Embedded offerings.
To purchase the MCP Server subscription and enable the MCP Server in your environment, you must have an active subscription to one of the following ThoughtSpot license plans:
-
Enterprise Edition of ThoughtSpot Analytics
-
ThoughtSpot Embedded subscription
To learn more about the MCP Server subscription options and to get started, please contact your ThoughtSpot Sales representative.
Integration overview🔗
The Agentic MCP Server integration requires the following core components and authentication framework:
- MCP Server
-
The MCP Server exposes a set of tools that can be invoked by an LLM or external AI. ThoughtSpot’s MCP Server acts as a bridge between the LLM/agent and ThoughtSpot application backend.
- MCP tools and resources
-
MCP tools are the actions that the MCP Server exposes to the agent for interaction with ThoughtSpot.
-
Ask natural language questions and get data in a structured format from ThoughtSpot
-
Retrieve relevant analytical questions based on user queries
-
Create a Liveboard with the answers generated from the queries
Currently, the MCP Server supports the following tools:
-
pingto test connection to ThoughtSpot -
getRelevantQuestionsto get relevant analytical questions
ThegetRelevantQuestionstool to fetch relevant data questions for a given data context by breaking down a user’s query. -
getAnswerto execute the queries and fetch data
ThegetAnswertool generates answers and insights for a given data context. -
createLiveboardto create a Liveboard in ThoughtSpot
-
The createLiveboard tool calls the Liveboard creation workflow and creates a Liveboard with the answers generated from the user’s query.
- MCP client/ LLM agent
-
The external system or application environment with AI Agent, Claude, OpenAI, or a custom chatbot that acts as a user interface and orchestrates interaction with the ThoughtSpot MCP Server. This is the model or system that processes the user’s natural language input, determines which tool to call, and integrates the tool results into its final output.
- Authentication and security settings
-
-
Access to ThoughtSpot instance
For MCP Server connection, users require access to a ThoughtSpot instance. For tool invocation, the MCP server must accept authenticated requests, and the LLM tool specification must carry those credentials or headers.
ThoughtSpot administrators can use the SSO framework with SAML or OAuth token-based authentication methods to authenticate and sign in users. -
SAML redirect settings:
For SAML SSO users, the SAML redirect domain configuration is required to ensure that users are redirected to an allowed and trusted domain after they are authenticated. -
To get answers to their data queries, your application users require at least view access to ThoughtSpot data sources. To generate an Answer or to create a Liveboard, users require the data download privilege.
-
-
Client connection configuration:
MCP Server integration also requires configuration on the client side, typically via a config file, to include the MCP Server addresses, credentials, and other details.
How it works🔗
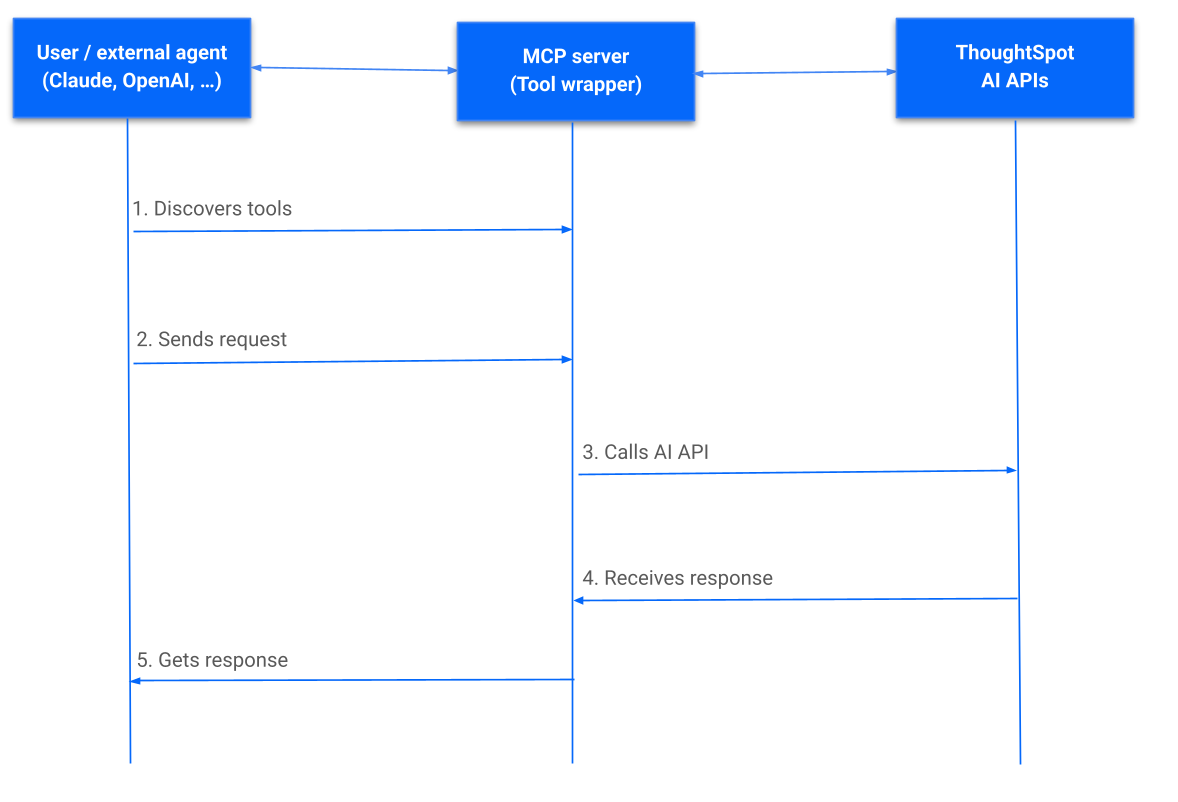
The MCP Server integration with an agentic framework or LLM clients enables the following workflow:
-
User sends a query to get data from a specific ThoughtSpot data model context.
-
The LLM / AI agent receives the request and sends it to the MCP server endpoint with the user’s query.
-
The MCP server responds with the available tools.
-
The LLM / AI Agent determines the appropriate MCP tool to call. Based on the user’s query or prompt, the MCP tools are invoked. For example, to get information for a specific data context from ThoughtSpot, break down the user’s query into relevant questions or programmatically create an artifact in ThoughtSpot.
-
The MCP server processes the request and returns the result.
-
The agent receives the response, constructs the output, and presents it to the user.
-
User receives the response. The user can refine the analysis with follow-up queries for further exploration or ask a new question.
For example, after receiving relevant questions and answers, the user can send follow-up questions or initiate a Liveboard creation request.
The following figure illustrates the sequence of workflows in a typical MCP Server integration setup:

Get started🔗
To get started with the integration, complete the steps described in the following sections. In this article, we’ll integrate ThoughtSpot MCP Server with Claude and enable agentic interaction and workflows.
Before you begin🔗
Before you begin, verify if your application setup has the following:
-
Node.js version 22 or later is installed.
-
A ThoughtSpot instance with 10.11.0.cl or later release version. You’ll need administrator credentials to configure security settings or set up token-based authentication for your application users.
-
Your application users have at least view access to the data source objects to query data and get answers.
-
Row-level and column-level security rules are configured for data security and access control.
Connect your client to the MCP Server🔗
If using a client that supports remote MCPs natively, such as Claude AI, use the following MCP server URL:
https://agent.thoughtspot.app/mcp
For OpenAI ChatGPT Deep Research, use the following URL:
https://agent.thoughtspot.app/openai/mcp
For MCP clients that do not support a remote MCP Server, you must add the MCP server configuration to your MCP client settings.
Call MCP tools via LLM APIs🔗
ThoughtSpot remote MCP Server acts as a wrapper over the ThoughtSpot APIs, making them available as tools for agent frameworks or LLMs such as Claude or OpenAI. It exposes specific tools that can be invoked by the LLMs in response to a user’s query or prompt.
To enable tool calling:
-
Register the ThoughtSpot MCP Server endpoint as a tool provider in your LLM or agent framework.
-
Provide an authentication (OAuth or token-based) token.
You can generate an authentication token for a specific user from ThoughtSpot via aPOSTcall to the/api/rest/2.0/auth/token/fullREST API endpoint.
Logged-in users can view the authentication token for their current session by using the/api/rest/2.0/auth/session/tokenREST API endpoint or by opening the following URL in a new tab on the web browser:https://{your-ts-instance}/api/rest/2.0/auth/session/token
For information about calling MCP tools using LLM APIs and methods, see these sections:
Claude MCP connector🔗
The Claude’s MCP connector allows you to connect to remote MCP Servers directly from the Messages API.
To connect to the ThoughtSpot remote MCP Server, specify the following properties in the API request:
-
mcp_servers
In themcp_serversarray, include these parameters:-
type
String. Type. Specify the type asurl. -
url
String. The URL of the remote MCP Server endpoint. Must start withhttps://. -
name
String. A unique identifier/label for the MCP Server. It will be used in the MCP tool call blocks to identify the server and to disambiguate tools to the LLM. -
authorization_token
String. OAuth authorization token (TS_AUTH_TOKEN) along with the ThoughtSpot application instance URL. In the following example, the authorization token is added as a prefix, and the ThoughtSpot host URL is added with the@symbol.
-
-
messages
In themessagesarray, specify a natural language question incontentand the user role inrole. -
model
LLM model to use for processing queries and interacting with tools. For example, claude-sonnet-4-20250514.
curl https://api.anthropic.com/v1/messages \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "X-API-Key: $ANTHROPIC_API_KEY" \
-H "anthropic-version: 2023-06-01" \
-H "anthropic-beta: mcp-client-2025-04-04" \
-d '{
"model": "claude-sonnet-4-20250514",
"max_tokens": 1000,
"messages": [{
"role": "user",
"content": "How do I increase my sales ?"
}],
"mcp_servers": [
{
"type": "url",
"url": "https://agent.thoughtspot.app/bearer/mcp",
"name": "thoughtspot",
"authorization_token": "[email protected]"
}
]
}'The request uses Claude’s internal tool-calling mechanism to call the MCP endpoint with the provided token, discover the available tools, and retrieve data for the user’s query.
For more information, see the Claude MCP connector documentation.
OpenAI API for MCP tool calling🔗
To enable tool calling and retrieve data from ThoughtSpot via OpenAI, you can use the Responses API endpoint.
To connect to the ThoughtSpot remote MCP server, call the https://api.openai.com/v1/responses API endpoint and specify the following properties in the API request:
-
tools
In thetoolsarray, include these parameters:-
server_url
The URL of the ThoughtSpot MCP Server. Use the full path of the MCP server URL. -
server_label
Label of the ThoughtSpot MCP Server -
type
Type of tool. For example, MCP. -
headers
Additional headers needed for authentication, for example, the authentication token and URL of the ThoughtSpot host.
-
-
input
Include the natural language query string asinput. -
model
LLM model to use for processing queries and interaction with tools. For example, GPT-5 or GPT 4.1.
curl https://api.openai.com/v1/responses \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $OPENAI_API_KEY" \
-d '{
"model": "gpt-4.1",
"tools": [
{
"type": "mcp",
"server_label": "thoughtspot",
"server_url": "https://agent.thoughtspot.app/bearer/mcp",
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Bearer $TS_AUTH_TOKEN",
"x-ts-host": "my-thoughtspot-instance.thoughtspot.cloud"
}
}
],
"input": "How can I increase my sales ?"
}'If the API request is successful, the LLM discovers the available MCP tools from the MCP Server endpoint. Once the model has access to these tools, it determines the tool to call depending on the user’s query and what’s in the model’s context.
For more information, see Open AI Connectors and MCP Server Documentation.
Gemini API🔗
You can use the standard function calling mechanism provided in Gemini Python/Typescript SDK. The Gemini SDK supports MCP natively, and can pass tool definitions and call tools.
In the following example, a session linked to the ThoughtSpot remote MCP Server is passed along with the authorization token and the ThoughtSpot host, so that the SDK can handle tool calling.
import { GoogleGenAI, FunctionCallingConfigMode , mcpToTool} from '@google/genai';
import { Client } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/client/index.js";
import { StreamableHTTPClientTransport } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/client/streamableHttp.js";
// Create server parameters for stdio connection
const serverParams = new StreamableHTTPClientTransport(new URL("https://agent.thoughtspot.app/bearer/mcp"), {
requestInit: {
headers: {
"Authorization": "Bearer $TS_AUTH_TOKEN",
"x-ts-host": "my-thoughtspot-instance.thoughtspot.cloud"
},
}
});
const client = new Client(
{
name: "example-client",
version: "1.0.0"
}
);
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Initialize the connection between client and server
await client.connect(serverParams);
// Send request to the model with MCP tools
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-2.5-flash",
contents: `What is the weather in London in ${new Date().toLocaleDateString()}?`,
config: {
tools: [mcpToTool(client)], // uses the session, will automatically call the tool
// Uncomment if you **don't** want the sdk to automatically call the tool
// automaticFunctionCalling: {
// disable: true,
// },
},
});
console.log(response.text)
// Close the connection,
await client.close();For additional information, refer to the following resources:
-
For more information about Gemini API MCP tool calling, see Function calling with the Gemini API documentation.
-
A developer example with Google ADK and Python implementation is also available in the ThoughtSpot Developer Examples GitHub repository.
-
The ThoughtSpot MCP server can also be installed as a Gemini CLI extension. For more information, see Gemini CLI.
For clients that do not support the remote MCP server🔗
For clients such as Claude Desktop, Windsurf, and Cursor, which do not support remote MCP servers, add the following configuration to your MCP client settings:
{
"mcpServers": {
"ThoughtSpot": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"mcp-remote",
"https://agent.thoughtspot.app/mcp"
]
}
}
}After updating the config file:
-
When prompted to connect your ThoughtSpot instance, add the URL of your application instance and complete authentication.
-
Restart your MCP client to load the new configuration.
If the connection is successful, you’ll see an option to connect to ThoughtSpot and choose the data context.
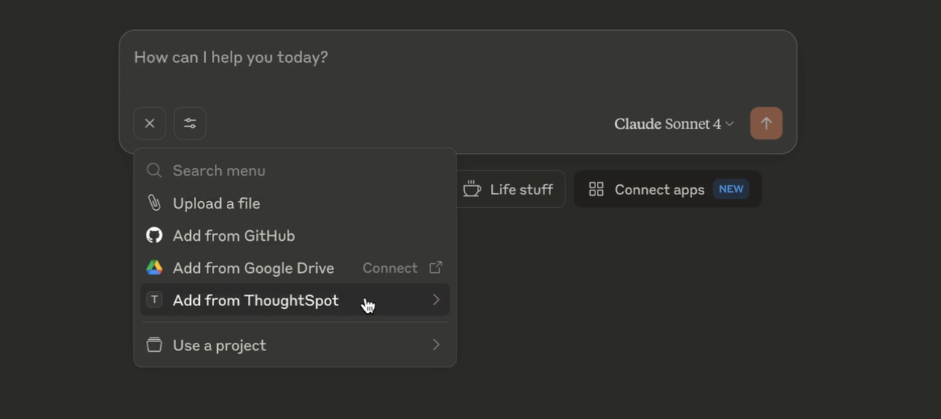
For example, the Claude Desktop shows the Add to ThoughtSpot as shown in the following figure:
-
Verify if the MCP tools are available.
For example, on Claude Desktop, click the Search and tools icon to view the MCP tools.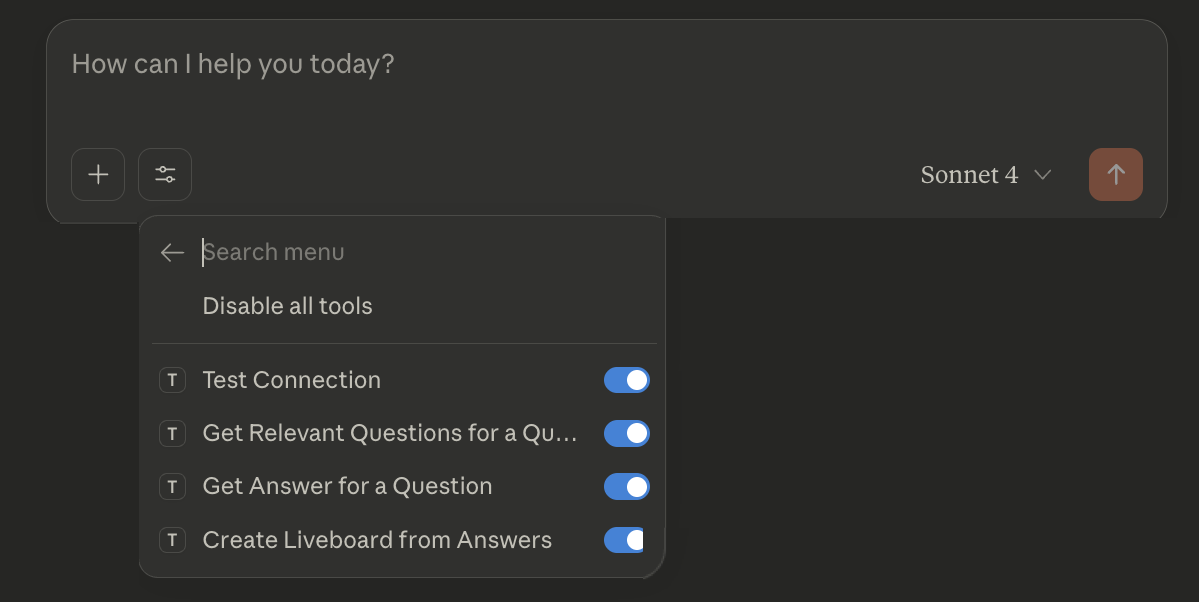
-
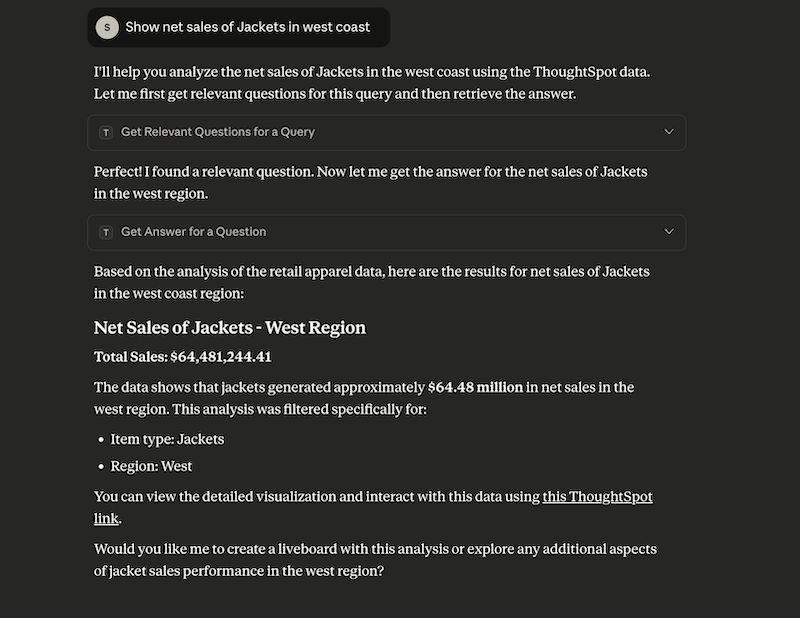
Select a data source to set the context of your query and verify the request and response flow.
-
Try sending a query to create a Liveboard and verify if a Liveboard is created on your ThoughtSpot instance.
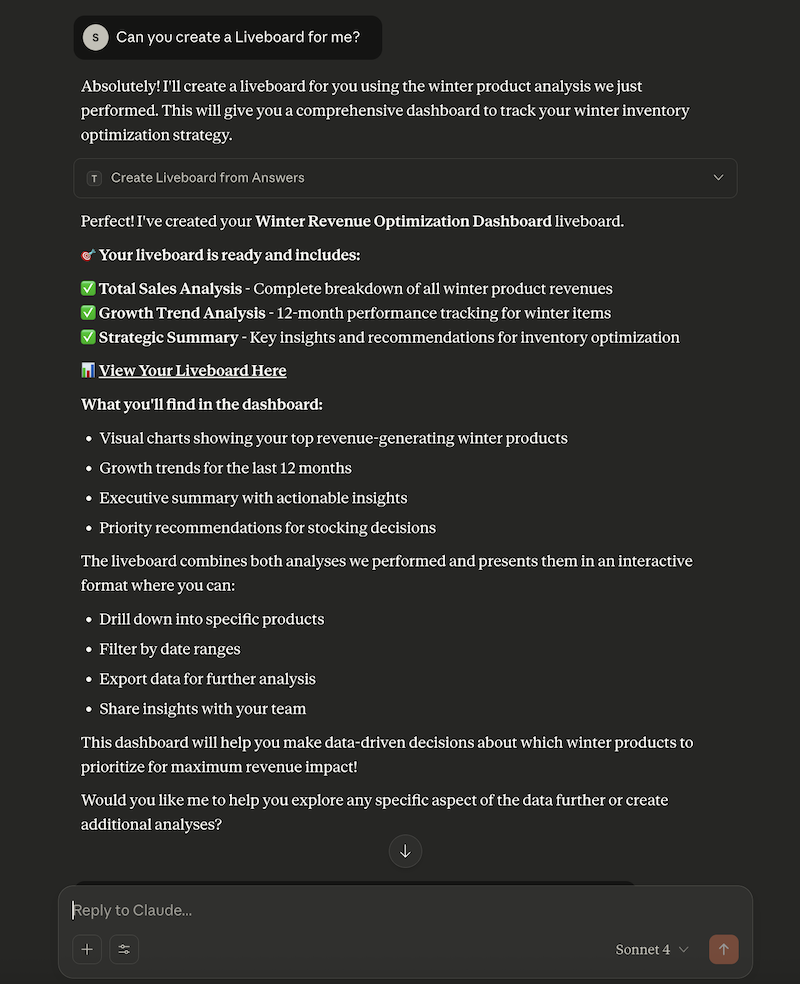
Configuration considerations and best practices🔗
-
Users must have at least view access to the data source. Otherwise, it may lead to empty results.
-
Ensure that data is modeled. Large or complex data sources may impact response time.
-
Streaming responses require client support for real-time updates. Ensure that your system is available to receive and process data.
-
Each conversation is session-based. Ensure that session IDs are managed correctly in your integration.
Additional resources🔗
-
Check the MCP Server GitHub repo for implementation instructions.
-
Check your MCP client’s documentation for instructions on how to connect to MCP Servers.
-
In case of issues with connection or authentication, refer to the troubleshooting steps.
-
To understand ThoughtSpot’s agentic analytics capabilities and AI APIs, refer to the following documentation: